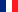
Apart from agriculture, the main resources of Viterbo's area are pottery, marble, and wood. The town also hosts the Italian gold reserves, an important Academy of Fine Arts, and the University of Tuscia, and is located in a wide thermal area, attracting many tourist from the whole central Italy.
 Although Viterbo is very ancient, its precise origins are unknown. According to the notorious forger, Annio of Viterbo, it originated as anEtruscan town. At any rate, on the present site of Viterbo, or nearby, there was a little Roman colony (Vicus Elbii); whether this is the same center referred to as Vetus Urbs ("Old City") in the Middle Ages is uncertain.
Although Viterbo is very ancient, its precise origins are unknown. According to the notorious forger, Annio of Viterbo, it originated as anEtruscan town. At any rate, on the present site of Viterbo, or nearby, there was a little Roman colony (Vicus Elbii); whether this is the same center referred to as Vetus Urbs ("Old City") in the Middle Ages is uncertain.
The first firm report of the new city dates to the eighth century, when it is identified as Castrum Viterbii. It was fortified in 773 by the Lombard king Desiderius in his vain attempt to conquer Rome. When the Popes switched to the Frankish support, Viterbo became part of the Papal States, but this status was to be highly contested by the Emperors in the following centuries, until in 1095 it is known it was a free comune.
In a period in which the Popes had difficulties asserting their authority over Rome, Viterbo became their favourite residence, beginning with Pope Eugene III (1145-1146) who was besieged in vain in the city walls. In 1164 Frederick Barbarossa made Viterbo the seat of hisAntipope Paschal III. Three years later he gave it the title of "city" and used its militias against Rome. In 1172 Viterbo started its expansion, destroying the old city of Ferentum and conquering other lands: in this age it was a rich and prosperous comune, one of the most important of Central Italy, with a population of almost 60,000.
In 1207, Pope Innocent III held a council in the cathedral, but the city was later excommunicated as favourite seat of the heretical Patari and even defeated by the Romans. In 1210, however, Viterbo managed to defeat the Emperor Otto IV and was again in war against Rome.
In the thirteenth century it was ruled alternately by the tyrants of the Gatti and Di Vico families. Frederick II drew Viterbo to the Ghibelline side in 1240, but when the citizens expelled his turbulent German troops in 1243 he returned and besieged the city, but in vain. From that point Viterbo was always a loyal Guelph. Between 1257 and 1261 it was the seat of Pope Alexander IV, who also died here. His successorUrban IV was elected in Viterbo.
In 1266-1268 Clement IV chose Viterbo as the base of his ruthless fight against the Hohenstaufen: here, from the loggia of the Papal Palace, he excommunicated the army of Conradin of Swabia which was passing on the Via Cassia, with the prophetical motto of the "lamb who is going to the sacrifice". Other popes elected in Viterbo were Gregory X (1271) and John XXI (1276) (who died in the Papal Palace when the ceiling of the recently-built library collapsed on him while he slept), Nicholas III and the French Martin IV. The Viterbese, who did not agree with the election of a foreigner directed by the King of Naples, Charles I of Anjou, invaded the cathedral where the conclave was held, arresting two of the cardinals. They were subsequently excommunicated, and the Popes avoided Viterbo for 86 years.
Without the Popes, the city fell into the hands of the Di Vicos. In the fourteenth century, Giovanni di Vico had created a seignory extending to Civitavecchia, Tarquinia, Bolsena, Orvieto, Todi, Narni and Amelia. His dominion was crushed by Cardinal Gil de Albornoz in 1354, sent by the Avignonese popes to recover the Papal States, who built the Castle. In 1375 the city gave its keys to Francesco Di Vico, son of the previous tyrant, but thirteen years later the people killed him and assigned the city first to Pope Urban VI, and then to Giovanni di Sciarra di Vico, Francesco's cousin. But Pope Boniface IX's troops drove him away in 1396 and established a firm Papal suzerainty over the city. The last Di Vico to hold power in Viterbo was Giacomo, who was defeated in 1431.
Thenceforth Viterbo became a city of secondary importance, following the vicissitudes of the Papal States. In the 16th century it was the birthplace of Latino Latini. It becoming part of Italy in 1871.
Main Sights
Viterbo's historic center is one of the best preserved medieval towns of central Italy. Many of the older buildings (particularly churches) are built on top of ancient ruins, recognizable by their large stones, 50 centimeters to a side.
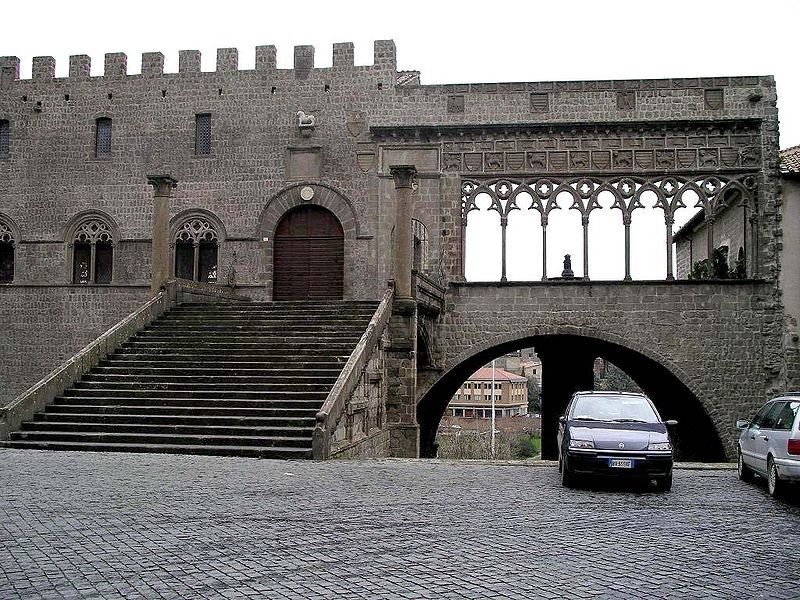
The main attraction of Viterbo is the Papal Palace (Palazzo dei Papi), that served as a country residence and a repair in time of trouble in Rome. The columns of the palace are spolia from a Roman temple.
The second most important monument of the city is the Cathedral of S. Lorenzo. It was erected in Romanesque style by Lombard architects over a temple of Hercules. It was variously rebuilt from the sixteenth century on, and was heavily damaged in 1944 by Allied bombs. The notable Gothic belfry is from the first half of the fourteenth century, and shows influence of Senese artists. The church houses the sarcophagus of Pope John XXI and the picture Christ Blessing by Gerolamo da Cremona (1472).
Other notable monuments are:
- The Palazzo Comunale (begun 1460), Palazzo del Podestà (1264) and Palazzo della Prefettura (rebuilt 1771) on the central square Piazza del Plebiscito. The Palazzo Comunale houses a series of sixteenth century and Baroque frescoes by Tarquinio Ligustri, Bartolomeo Cavarozzi and others.
- The small Gothic church of Santa Maria della Salute, which has a rich portal.
- The Romanesque Chiesa del Gesù (eleventh century). Here the sons of Simon de Montfort stabbed to death Henry of Almain, son of Richard of Cornwall.
- The Palazzo Farnese (fourteenth-fifteenth century), where Alessandro Farnese, the future Pope Paulus III, lived in his youth together with his beautiful sister, Giulia Farnese.
- The Rocca (castle).
- The Romanesque churches of Santa Maria Nuova (twelfth century), San Sisto (second half of the ninth century), and San Giovanni in Zoccoli (eleventh century).
- The Palazzo degli Alessandri in the old district, a typical patrician house of Middle Ages Viterbo.
- The Fontana Grande (Big fountain) on the homonymous square
- The Fontana Grande, begun in 1206.
- The Gothic church of San Francesco, built over a pre-existing Lombard fortress. It has a single nave with Latin cross plan. It houses the sepulchre of Pope Adrian V, who died in Viterbo on August 17, 1276, considered the first monument by Arnolfo di Cambio.
- The Museo Civico (City Museum) houses many archeological specimens from the pre-historical to Roman times, plus a Pinacoteca (gallery) with paintings of Sebastiano del Piombo, Antoniazzo Romano, Salvator Rosa, Antiveduto Grammatica and others. The Orto Botanico dell'Università della Tuscia is a botanical garden operated by the university.
Patron saints
Santa Maria Rosa is the patron saint of Viterbo. The legend of Santa Rosa is that she helped to eradicate those few who supported the emperors instead of the Popes, around 1250. San Lorenzo is the male patron saint. A native of Viterbo, Blessed Dominic Barberi, was born on 22 June 1792 and would later minister in England.
Macchina di Santa Rosa
The transport of the Macchina di S. Rosa takes place every year, on September 3, at 9 o'clock in the evening. The Macchina is an artistic illuminated bell-tower with an imposing height of 30 m. It weighs between 3.5 and 5 tonnes and is made of iron, wood and papier-mâché. At the top of the tower, the statue of the Patron Saint is enthusiastically acclaimed by the people in the streets of the town centre, where lights are turned off for the occasion. One hundred and thirty Viterbesi men (known as the Facchini) carry the Macchina from Porta Romana through the each of the major streets of Viterbo, concluding with a strenuous ascension up to the Piazza di Santa Rosa, its final resting place. Each Macchina has a life span of five years, after which a new one is built.
Coat of arms

Airport
Viterbo currently has a small military air force base, located 3 km from the town. On November 26, 2007, Italian transport minister Alessandro Bianchi announced that Viterbo had been chosen as the site of the next Airport in Lazio to serve Rome, over Latina, Frosinone, and Guidonia.