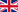
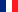
Epiphany (from Koine Greek ἐπιφάνεια "appearance", "manifestation") is a Christian feast day which celebrates the revelation of God in human form in the person of Jesus Christ. It falls on January 6 or on a Sunday close to that date. January 6 in the Julian Calendar, which is followed by some Eastern Churches, corresponds at present to January 19 in the Gregorian Calendar, which is the official civil calendar in most countries. On this day, Western Christians commemorate principally the visitation of the Biblical Magi to the child Jesus, i.e., his manifestation to the Gentiles; Eastern Christians commemorate the baptism of Jesus in the Jordan River, seen as his manifestation to the world as the Son of God. It is also called Theophany, especially by Eastern Christians.
Epiphany (from Koine Greek ἐπιφάνεια "appearance", "manifestation") is a Christian feast day which celebrates the revelation of God in human form in the person of Jesus Christ. It falls on January 6 or on a Sunday close to that date. January 6 in the Julian Calendar, which is followed by some Eastern Churches, corresponds at present to January 19 in the Gregorian Calendar, which is the official civil calendar in most countries. On this day, Western Christians commemorate principally the visitation of the Biblical Magi to the child Jesus, i.e., his manifestation to the Gentiles; Eastern Christians commemorate the baptism of Jesus in the Jordan River, seen as his manifestation to the world as the Son of God. It is also called Theophany, especially by Eastern Christians.
The observance had its origins in the Eastern Christian Churches, and was a general celebration of the Incarnation of Jesus Christ. It included the commemoration of: his birth; the visit of the Magi ("Wise Men", as Magi were Persian priests) to Bethlehem; all of Jesus' childhood events, up to and including his baptism in the Jordan byJohn the Baptist; and even the miracle at the Wedding of Cana in Galilee. It seems fairly clear that the Baptism was the primary event being commemorated.
Christians fixed the date of the feast on January 6 quite early in their history. Ancient liturgies noted Illuminatio, Manifestatio, Declaratio (Illumination, Manifestation, Declaration); cf. Matthew 3:13–17; Luke 3:22; and John 2:1–11; where the Baptism and the Marriage at Cana were dwelt upon. Western Christians have traditionally emphasized the "Revelation to the Gentiles" mentioned in Luke, where the term Gentile means all non-Jewish peoples. The Biblical Magi, who represented the non-Jewish peoples of the world, paid homage to the infant Jesus in stark contrast to Herod the Great (King of Judea), who sought to kill him. In this event, Christian writers also inferred a revelation to the Children of Israel. Saint John Chrysostom identified the significance of the meeting between the Magi and Herod's court: "The star had been hidden from them so that, on finding themselves without their guide, they would have no alternative but to consult the Jews. In this way the birth of Jesus would be made known to all."
The earliest reference to Epiphany as a Christian feast was in A.D. 361, by Ammianus Marcellinus St. Epiphanius says that January 6 is hemera genethlion toutestin epiphanion (Christ's "Birthday; that is, His Epiphany").[6] He also asserts that the Miracle at Cana occurred on the same calendar day.[7]
In 385, the pilgrim Egeria (also known as Silvia) described a celebration in Jerusalem and Bethlehem, which she called "Epiphany" (epiphania) that commemorated the Nativity of Christ. Even at this early date, there was an octave associated with the feast.
In a sermon delivered on December 25, 380, St. Gregory of Nazianzus referred to the day as ta theophania ("the Theophany", an alternative name for Epiphany), saying expressly that it is a day commemorating he hagia tou Christou gennesis ("the holy nativity of Christ") and told his listeners that they would soon be celebrating the baptism of Christ. Then, on January 6 and 7, he preached two more sermons, wherein he declared that the celebration of the birth of Christ and the visitation of the Magi had already taken place, and that they would now commemorate his Baptism. At this time, celebration of the two events was beginning to be observed on separate occasions, at least in Cappadocia.
Saint John Cassian says that even in his time (beginning of the 5th century), the Egyptian monasteries celebrated the Nativity and Baptism together on January 6. The Armenian Apostolic Church continues to celebrate January 6 as the only commemoration of the Nativity.
Epiphany is celebrated by both the Eastern and Western Churches, but a major difference between them is precisely which events the feast commemorates. For Western Christians, the feast primarily commemorates the coming of the Magi; Eastern churches celebrate the Baptism of Christ in the Jordan. In both traditions, the essence of the feast is the same: the manifestation of Christ to the world (whether as an infant or in the Jordan), and the Mystery of the Incarnation.
Western Christian Churches
Even before the year 354, the Western Church had separated the celebration of the Nativity of Christ as the feast of Christmas and set its date as December 25; it reserved January 6 as a commemoration of the manifestation of Christ, especially to the Magi, but also at his baptism and at the wedding feast of Cana. Hungarians, in an apparent reference to baptism, refer to the January 6 celebration as Vízkereszt or "water cross". In parts of the Eastern Church, January 6 continued for some time as a composite feast that included the Nativity of Jesus: though Constantinople adopted December 25 to commemorate Jesus' birth in the fourth century, in other parts the Nativity of Jesus continued to be celebrated on January 6, a date later devoted exclusively to commemorating his Baptism.
Liturgical practice in Western Churches
The West historically observed a twelve-day festival, starting on December 25, and ending on January 5, known as Christmastide or the twelve days of Christmas. Some Christian cultures, especially those of Latin America and some in Europe, extend the season to as many as forty days, ending on Candlemas (February 2).
On the Feast of the Epiphany, the priest, wearing white vestments, will bless the Epiphany water, frankincense, gold, and chalk. Chalk is used to write the initials of the three magi over the doors of churches and homes. The letters stand for the initials of the Magi (traditionally named Caspar, Melchior, and Balthasar), and also the phrase Christus mansionem benedicat, which translates as "may Christ bless the house".
According to ancient custom, the priest announced the date of Easter on the feast of Epiphany. This tradition dated from a time when calendars were not readily available, and the church needed to publicize the date of Easter, since many celebrations of the liturgical year depend on it. The proclamation may be sung or proclaimed at the ambo by a deacon, cantor, or reader either after the reading of the Gospel or after the postcommunion prayer.
Date of commemoration
Prior to the reform of 1955, when Pope Pius XII abolished all but three liturgical octaves, the Roman Catholic Church celebrated Epiphany as an eight-day feast beginning on January 6 and ending on January 13, known as the Octave of Epiphany. They celebrated the feast of the Holy Family on the Sunday within the octave, and the Feast of the Holy Name of Jesus on the Sunday between January 2 and January 5 or, if there were no such Sunday, on January 2. They calculated Christmastide as the twelve days ending on January 5, followed by Epiphany time, consisting of the feast and its octave.
In the 1970 revision of the Roman Catholic calendar of saints, Epiphany is celebrated on January 6 for countries where the feast is a Holy Day of Obligation. In other countries, it is celebrated on the Sunday after January 1. Christmastide ends with the feast of the Baptism of the Lord, which is always on the Sunday after Epiphany (unless, where Epiphany is not a holy day of obligation, Epiphany is celebrated on January 7 or 8, in which case Baptism of the Lord is celebrated in the following Monday).
The Roman Missal provides a formula with appropriate chant (in the tone of the Exsultet) for proclaiming on Epiphany, wherever it is customary to do so, the dates in the calendar for the celebration of Ash Wednesday, Easter Sunday, Ascension of Jesus Christ, Pentecost, the Body and Blood of Christ, and the First Sunday of Advent in the following Liturgical Year.
Prior to 1976, the Anglican churches also observed an eight-day feast. Today the Epiphany is classified as a Principal Feast and is observed on January 6 or on the Sunday between January 2 and 8. There is also an Epiphany season, observed between the season of Christmas and the first period of Ordinary Time. It begins at Evening Prayer on the Eve of the Epiphany and ends at Evening Prayer on the Feast of the Presentation (which may be celebrated on February 2 or on the Sunday between January 28 and February 3).
There are varying stories about Epiphany and Italy. According to the Roman author Macrobius, the word "Epiphania" was transformed into Befana, the great fair held at that season, when sigillaria of terracotta or baked pastry were sold (Macrobius I, x, xxiv; II, xlix). In popular folklore, Befana visits all the children of Italy on the eve of January 6 to fill their socks with candy and presents if they are good or a lump of coal or dark candy if they are bad.
In some European cultures, the greenery put up at Christmas is taken down at Epiphany, in other cultures it remains up until the Presentation of Jesus at the Temple (February 2).
The Irish call this day Little Christmas or "Women's Christmas" (Irish: Nollaig na mBan).
The Dutch and Flemish call this day Drie Koningen (Three Kings' Day). In the Netherlands and Belgium, children in groups of three (symbolising the three kings) proceed in costume from house to house while singing songs typical for the occasion, and receiving a coin or some sweets at each door.
In France, on Epiphany people eat the gâteau des Rois in Provence or the galette des Rois in the northern half of France and Belgium. This is a kind of king cake, with a trinket (usually a porcelain figurine of a king) or a bean hidden inside. The person who gets the piece of cake with the trinket becomes "king" for a day.
In Greece, Cyprus and the Greek diaspora throughout the world, the feast is colloquially called the "Phōta" (Greek: Φώτα, "Lights") and customs revolve around the Great Blessing of the Waters. It marks the end of the traditional ban on sailing, as the tumultuous winter seas are cleansed of the mischief-prone "kalikántzaroi", the goblins that try to torment God-fearing Christians through the festive season. The Phota form the middle of another festive triduum, together with Epiphany Eve, January 5, when children sing the Epiphany carols, and the great feast of St. John the Baptist on January 7, when the numerous Johns and Joans celebrate their name-day.
In Malta, Epiphany is commonly known as It-Tre Re (The Three Kings). Until the 1980s January 6 was a public holiday, but today the Maltese are celebrating Epiphany on the first Sunday of the year. But children are still taking January 6 as a school holiday and Christmas decorations light up till this day also on most public streets.
In Portugal, Epiphany, on January 6, is called dia dos Reis (day of the kings), during which the traditional Bolo Rei (King cake) is baked and eaten.
In Spain, and some Latin American countries Epiphany day is called El Día de los Reyes (The Day of the Kings), i.e., the day when a group of Kings or Magi, as related in the second chapter of the gospel of Matthew, arrived to worship and bring three gifts to the baby Jesus after following a star in the heavens. This day is sometimes known as the Día de los Tres Reyes Magos (The day of the Three Royal Magi) or La Pascua de los Negros (Holy Day of the Blackmen) in Chile, although the latter is rarely heard. In Spanish tradition, on the day of January 6, three of the Kings: Melchor, Gaspar, and Balthazar, representing Europe, Arabia, and Africa, arrived on horse, camel and elephant, bringing respectively gold, frankincense and myrrh to the baby Jesus. Children (and many adults) polish and leave their shoes ready for the Kings' presents before they go to bed on the eve of January 6. Sweet wine, nibbles, fruit and milk are left for the Kings and their camels. In Mexico, it is traditional for children to leave their shoes, along with a letter with toy requests for the Three Kings, by the family nativity scene or by their beds. In some parts of northern Mexico the shoes and letters are left under the Christmas tree. The shoes may be filled with hay for the camels, so that the Kings will be generous with their gifts.
In the Philippines, the Christmas season traditionally ends on this day, known colloquially as "Three Kings" or "Tres Reyes" (Filipino:Tatlong Hari). Filipino children also leave their shoes out, so that the Kings would leave behind gifts like candy or money inside. Most others on this day simply greet one another with the phrase "Happy Three Kings!". In some locales, there is the practise of having three men, dressed as the Tatlong Hari, ride around on horseback, distributing trinkets and candy to the children of the area. The collective name for the group is immortalised as the Filipino surname Tatlonghari, and the Spanish name for the day has survived to the present in masculine given name Epifanio (e.g. Epifanio de los Santos).
In Puerto Rico, it is traditional for children to fill a box with grass or hay and put it underneath their bed, for the same reasons. These traditions are analogous to the customs of children leaving mince pies and sherry out for Father Christmas in Western Europe or leaving milk and cookies for Santa Claus in the United States.
In the afternoon or evening of the same day the ritual of the Rosca de reyes/Roscón de Reyes is shared with family and friends. The Rosca or Roscón is a type of pastry made with orange blossom water and butter, and decorated with candied fruit. Baked inside is a small doll representing the baby Jesus.
In Mexico, the person who finds the doll in their piece of rosca must throw a party on February 2, "Candelaria Day," offering tamales and atole (a hot sweet drink thickened with corn flour) to the guests.
In Spain, the bread is known as Roscón. Made with the same or similar items above; traditionally the roscón was simply a round, sweet bread with candied fruit on top, however, recently, different flavoured whipped creams are used as filling. The 'Jesus' doll evolved into a small toy similar to a Kinder Surprise it may also includes a bean. The person who gets the toy is then crowned king for the day, while the person who finds the bean is responsible for paying for the Roscon.